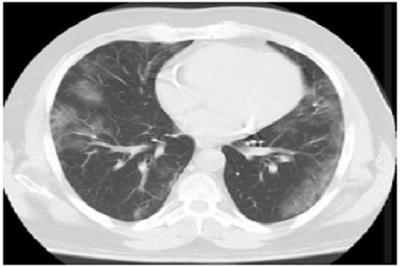
COVID as the name represents Coronavirus Disease which started as an outbreak in December 2019 in Hubei province of China and slowly and slowly transformed into global pandemic by mid-March 2020. Like for many other viral infections, RT-PCR has been the gold standard for the detection of viral RNA in the nasal and oropharyngeal swab specimens. However due to constant ongoing mutations in the viral genome, RTPCR has shown decreased sensitivity towards detection of viral RNA. This is where the HRCT scan of the lungs comes into picture, which allows direct visualization of the lung parenchyma affected by the virus. An objective CT severity score was formed to standardise CT reporting and to quantify the effect of virus on the lungs as follows:
Each of the lobes of lungs were evaluated for the extent of involvement with score of 0 representing no involvement, score of 1 representing <5 % involvement, score of 2 representing 5-25% involvement, score of 3 representing 25-50 % involvement, score of 4 representing 50-75 % involvement and score of 5 representing > 75 % involvement.
After quantifying each lobe on both sides, a total CT score is obtained (out of 25) which is the sum of CT scores of individual lobes. It has been found that CT score > 16 depicts increased severity of disease and more fatal outcome. A CT score > 20 has very high chances of progression into ARDS with high correlation with the bio-inflammatory markers.